Experiment 24 rate law and activation energy pre lab answers – In this pre-lab, we delve into the fascinating realm of chemical kinetics, exploring the concepts of rate laws and activation energy. These fundamental principles govern the rates of chemical reactions, shedding light on their behavior and providing a deeper understanding of the molecular processes that shape our world.
As we embark on this scientific journey, we will unravel the mathematical underpinnings of rate laws, deciphering the coefficients that reveal the stoichiometry and kinetics of reactions. Furthermore, we will delve into the concept of activation energy, a critical factor that influences the likelihood of reactions occurring.
By understanding these concepts, we gain invaluable insights into the dynamics of chemical transformations.
Rate Law Determination
Rate laws describe the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentrations of the reactants. They are mathematical equations that express the dependence of the reaction rate on the concentrations of the reactants raised to their respective orders.
For example, the rate law for the reaction:
aA + bB → cC
can be written as:
Rate = k[A]^x[B]^y
where k is the rate constant, and x and y are the orders of the reaction with respect to reactants A and B, respectively.
Activation Energy
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be supplied to a system in order for a chemical reaction to occur. It is a measure of the energy barrier that must be overcome for the reactants to form products.
Factors that influence activation energy include:
- The nature of the reactants
- The temperature
- The presence of a catalyst
Experimental Design
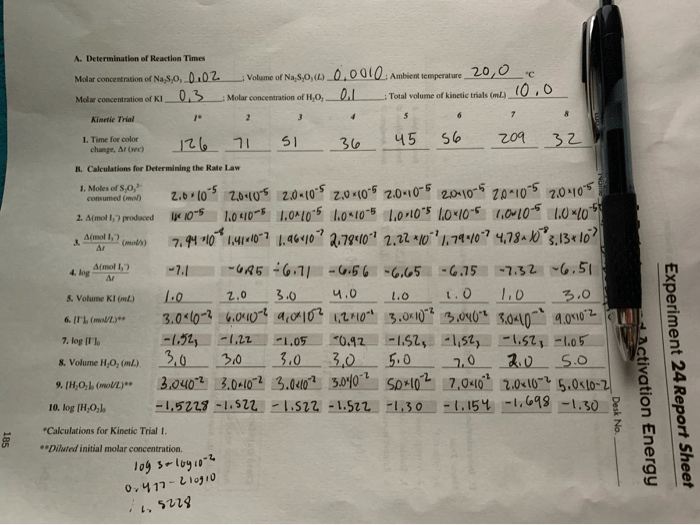
To determine the rate law and activation energy of a reaction, an experiment must be designed that allows for the measurement of the reaction rate at different concentrations of the reactants and temperatures.
It is important to control variables such as the temperature, volume, and surface area of the reaction vessel, as well as the purity of the reactants.
Appropriate measurement techniques must be used to accurately measure the concentrations of the reactants and products over time.
Data Analysis
The data from the experiment can be analyzed using graphs and mathematical equations to determine the rate law and activation energy.
Graphs of the reaction rate versus the concentrations of the reactants can be used to determine the orders of the reaction with respect to each reactant.
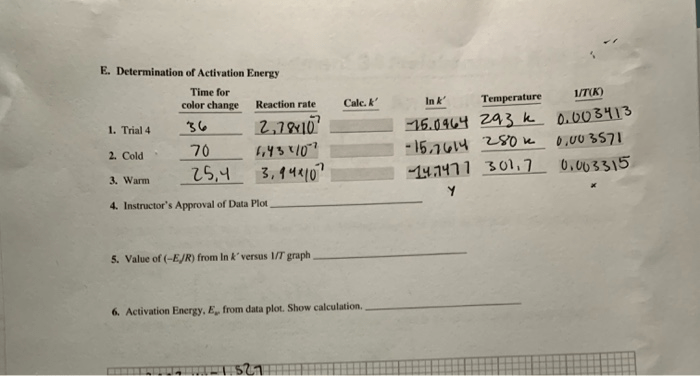
The Arrhenius equation can be used to determine the activation energy from a graph of the logarithm of the rate constant versus the inverse of the temperature.
Error Analysis, Experiment 24 rate law and activation energy pre lab answers
There are several sources of error in rate law and activation energy determinations, including:
- Measurement errors
- Instrumental errors
- Errors due to side reactions
It is important to minimize errors and assess the reliability of results by using appropriate experimental techniques and statistical analysis.
Questions Often Asked: Experiment 24 Rate Law And Activation Energy Pre Lab Answers
What is the significance of the coefficients in a rate law equation?
The coefficients in a rate law equation represent the stoichiometry of the reaction, indicating the relative number of moles of each reactant involved in the rate-determining step.
How does activation energy affect the rate of a reaction?
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required for a reaction to occur. A higher activation energy leads to a slower reaction rate.
What are some factors that influence activation energy?
Factors that influence activation energy include the nature of the reactants, the reaction mechanism, the presence of a catalyst, and the temperature.