In the realm of accounting, the meticulous process of problem 11-6 reconciling the bank statement holds paramount importance, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial records. This intricate procedure involves meticulously comparing the records maintained by a company with the corresponding bank statement, identifying and rectifying any discrepancies that may arise.
The significance of bank reconciliation extends far beyond mere compliance with accounting standards. It serves as a crucial tool for detecting potential errors or fraudulent activities, safeguarding the integrity of financial data, and enabling informed decision-making based on accurate information.
Bank Reconciliation Process
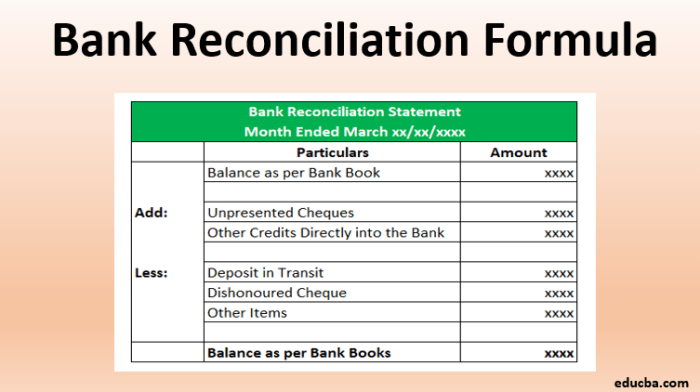
Bank reconciliation is the process of matching the transactions recorded in a company’s accounting records to the transactions recorded on its bank statement. This process ensures that the company’s cash balance matches the bank’s records and helps identify any errors or omissions in either set of records.
Step-by-Step Guide to the Bank Reconciliation Process
- Gather all relevant documents, including the bank statement, company check register, deposit slips, and canceled checks.
- Compare the bank statement balance to the company’s cash balance as of the statement date.
- Identify any outstanding checks or deposits that have not yet cleared the bank or been recorded in the company’s records.
- Investigate any differences between the bank statement and company records and make any necessary adjustments.
- Prepare a bank reconciliation statement that summarizes the adjustments made and reconciles the bank statement balance to the company’s cash balance.
Identifying and Correcting Differences
Common Reasons for Differences Between the Bank Statement and Company Records
- Outstanding checks: Checks written by the company that have not yet cleared the bank.
- Outstanding deposits: Deposits made by the company that have not yet been recorded by the bank.
- Bank errors: Errors made by the bank in processing transactions.
- Company errors: Errors made by the company in recording transactions.
How to Identify and Correct Errors or Omissions
To identify errors or omissions, compare the individual transactions on the bank statement to the corresponding transactions in the company’s records. Any discrepancies should be investigated and corrected.
Adjusting Journal Entries
Examples of Adjusting Journal Entries
- To record an outstanding check: Debit Bank and credit Accounts Payable.
- To record an outstanding deposit: Debit Accounts Receivable and credit Bank.
- To correct a bank error: Debit or credit Bank as needed to correct the error.
- To correct a company error: Debit or credit the appropriate account to correct the error.
Impact of These Entries on the Financial Statements
Adjusting journal entries impact the financial statements by correcting the cash balance and ensuring that the financial statements accurately reflect the company’s financial position.
Analysis of Reconciled Statement
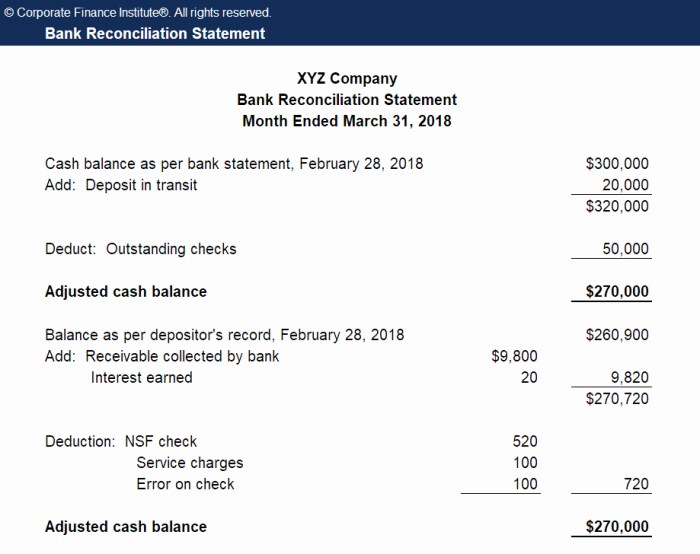
Importance of Reviewing the Reconciliation for Fraud Detection and Prevention
Reviewing the reconciled bank statement can help identify potential fraud by detecting unusual transactions or patterns.
Supporting Documentation
Importance of Maintaining Supporting Documentation
Supporting documentation provides evidence to support the bank reconciliation and helps prevent fraud.
Examples of Supporting Documents
- Bank statements
- Deposit slips
- Canceled checks
- Bank correspondence
Automation and Technology: Problem 11-6 Reconciling The Bank Statement

Benefits of Using Automation and Technology, Problem 11-6 reconciling the bank statement
- Reduces time and effort spent on reconciliation.
- Improves accuracy and reduces errors.
- Provides real-time access to bank data.
- Facilitates collaboration and data sharing.
Examples of Software or Tools
- Bank reconciliation software
- Accounting software
- Cloud-based reconciliation tools
Best Practices
Tips for Preventing Errors and Ensuring Accuracy
- Reconcile bank statements promptly.
- Use a systematic and consistent approach.
- Review reconciliations for unusual transactions or patterns.
- Maintain clear and organized supporting documentation.
- Use technology to automate and streamline the process.
FAQ Explained
What is the purpose of bank reconciliation?
Bank reconciliation ensures the accuracy and reliability of financial records by comparing company records with bank statements, identifying and correcting any discrepancies.
What are some common reasons for differences between the bank statement and company records?
Common reasons for differences include outstanding checks, deposits in transit, bank errors, and recording errors in the company’s books.
How can adjusting journal entries help reconcile the bank statement?
Adjusting journal entries are used to correct errors or omissions in either the bank statement or company records, bringing them into agreement.
What is the importance of supporting documentation in the reconciliation process?
Supporting documentation, such as bank statements, deposit slips, and canceled checks, provides evidence and traceability for the reconciliation process.
How can technology assist with bank reconciliation?
Technology, such as accounting software and automated reconciliation tools, can streamline the reconciliation process, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.