Activity 8.4 numerical dating of rocks and fossils – Activity 8.4: Numerical Dating of Rocks and Fossils embarks on an enlightening journey into the realm of geochronology, where we delve into the captivating techniques used to determine the age of ancient materials, unlocking the secrets of Earth’s history and the remnants of life that once flourished.
Numerical dating methods, such as radiometric dating, have revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s geological timeline and the evolution of life. By harnessing the principles of radioactive decay, scientists can decipher the age of rocks and fossils with remarkable precision, providing invaluable insights into the chronology of our planet and the history of life’s diversification.
Numerical Dating Techniques

Numerical dating techniques provide a means to determine the absolute age of rocks and fossils, providing invaluable insights into Earth’s history and the evolution of life.
Radiometric dating is a fundamental numerical dating technique that utilizes the decay of radioactive isotopes to estimate the age of geological materials. This method relies on the principle that radioactive isotopes decay at a constant rate, known as the half-life, which is specific to each isotope.
By measuring the ratio of a radioactive isotope to its stable daughter product, scientists can calculate the time elapsed since the rock or fossil formed.
Examples of radiometric dating methods include potassium-argon (K-Ar) dating, which is commonly used to date volcanic rocks and lava flows, and carbon-14 (C-14) dating, which is applicable to organic materials less than 50,000 years old.
Radiometric dating has revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s history, providing a chronological framework for geological events. It has enabled scientists to date geological formations, estimate the age of fossils, and reconstruct past climates and environments.
Applications in Geology and Paleontology: Activity 8.4 Numerical Dating Of Rocks And Fossils
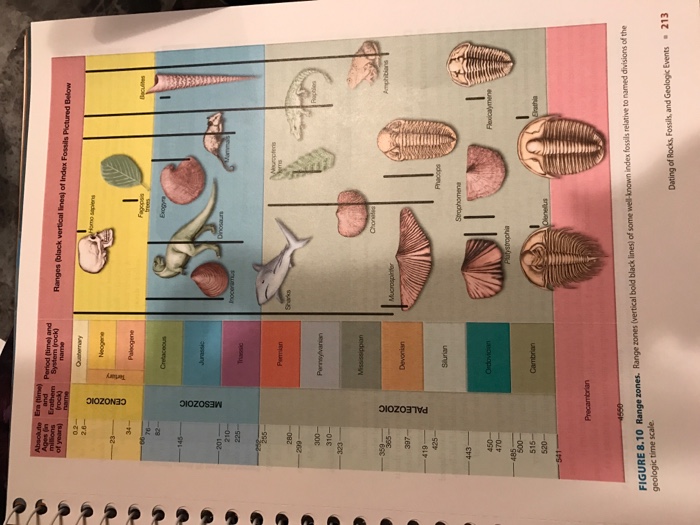
Numerical dating has made significant contributions to our understanding of Earth’s history and the evolution of life.
- Dating Geological Formations: Radiometric dating has allowed scientists to determine the age of rock formations and geological events, such as volcanic eruptions and mountain building.
- Dating Fossils: Numerical dating techniques have been instrumental in establishing the chronology of fossil-bearing strata, enabling paleontologists to reconstruct the evolutionary history of species and ecosystems.
- Reconstructing Past Climates and Environments: Numerical dating has provided valuable insights into past climates and environments by dating sedimentary rocks, ice cores, and other geological materials that preserve environmental information.
Limitations and Challenges

While numerical dating techniques provide powerful tools for dating rocks and fossils, they are not without limitations and challenges.
- Accuracy and Precision: The accuracy and precision of numerical dating methods depend on several factors, including the half-life of the radioactive isotope, the availability of suitable samples, and the potential for contamination or alteration of the sample.
- Assumptions and Uncertainties: Radiometric dating assumes that the decay rate of radioactive isotopes has remained constant throughout Earth’s history, which may not always be the case. Additionally, uncertainties in the measurement of isotope ratios can introduce errors into the age estimates.
- Conflicting or Inconclusive Results: In some cases, numerical dating techniques can yield conflicting or inconclusive results, particularly when dealing with complex geological processes or highly altered samples.
Ethical Considerations
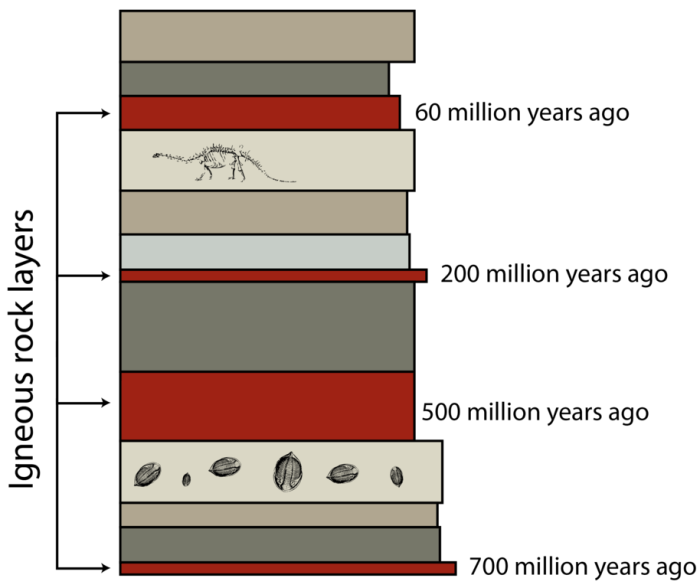
The use of numerical dating techniques raises ethical considerations related to the preservation of cultural heritage and the potential impact on historical narratives.
- Preservation of Cultural Heritage: Dating techniques can be invasive and potentially destructive to valuable artifacts or fossils, raising concerns about the preservation of cultural heritage.
- Historical Narratives: Numerical dating results can challenge or revise existing historical narratives, which may have cultural or religious significance. This can lead to debates and controversies about the interpretation of the past.
- Scientific Consensus and Peer Review: To ensure the reliability of numerical dating results, it is essential to rely on scientific consensus and peer review. This involves rigorous testing, replication of results, and open scientific discourse to minimize the risk of erroneous or biased interpretations.
FAQ Insights
What are the limitations of numerical dating methods?
Numerical dating methods can be affected by factors such as contamination, alteration, and resetting of the radioactive clock, which can introduce uncertainties into the age estimates.
How has numerical dating contributed to our understanding of Earth’s history?
Numerical dating has allowed us to determine the age of geological formations, such as mountain ranges and sedimentary basins, providing a framework for understanding the sequence of events in Earth’s history.
What are the ethical considerations associated with numerical dating?
The use of numerical dating to determine the age of fossils and artifacts can have implications for cultural heritage and historical narratives, raising ethical questions about the potential impact on cultural beliefs and practices.