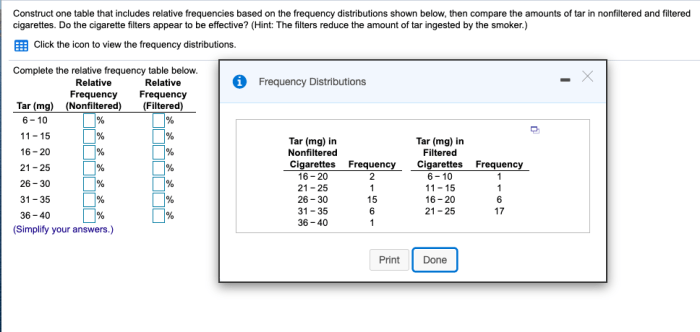
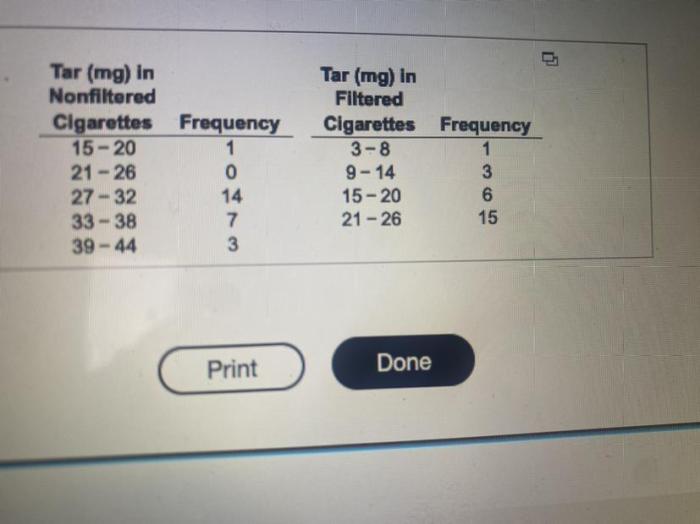
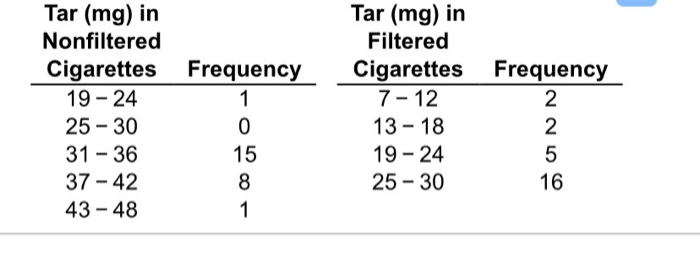
Construct one table that includes relative frequencies – In the realm of statistics, constructing a table of relative frequencies is a fundamental task that unveils valuable insights into data distribution. This comprehensive guide delves into the concept, calculation methods, and practical applications of relative frequencies, empowering you with the knowledge to create informative and accurate tables.
As we embark on this statistical journey, we will explore the theoretical foundations of relative frequencies, delve into the intricacies of calculation techniques, and uncover the significance of appropriate table formatting. Moreover, we will illuminate the diverse applications of relative frequencies, demonstrating their utility in various real-world scenarios.
1. Define and Explain Relative Frequencies
Relative frequencies are statistical measures that represent the proportion of times an event occurs within a sample or population. They are expressed as a decimal or percentage, ranging from 0 to 1 (or 0% to 100%). Relative frequencies help us understand the likelihood of an event occurring based on observed data.
To calculate relative frequencies, we divide the number of occurrences of an event by the total number of observations. The resulting value indicates the proportion of times the event occurred.
For example, if we flip a coin 10 times and observe 6 heads, the relative frequency of heads is 6/10 = 0.6 or 60%. This means that in the sample, heads occurred 60% of the time.
2. Methods for Calculating Relative Frequencies: Construct One Table That Includes Relative Frequencies

There are two main methods for calculating relative frequencies:
- Counting method:This involves manually counting the number of occurrences of an event and dividing it by the total number of observations.
- Formula method:This involves using the formula RF = f/N, where RF is the relative frequency, f is the number of occurrences of an event, and N is the total number of observations.
3. Constructing a Table of Relative Frequencies
A table of relative frequencies is a tabular representation of the relative frequencies of different events or categories. It helps organize and present the data in a clear and concise manner.
To construct a table of relative frequencies:
- List the different events or categories in the first column.
- Count the number of occurrences of each event or category.
- Calculate the relative frequency of each event or category using the counting or formula method.
- Organize the data in a table with columns for the event or category, number of occurrences, and relative frequency.
4. Applications of Relative Frequencies
Relative frequencies are widely used in various fields, including:
- Statistics:To analyze data, draw inferences, and make predictions.
- Probability:To estimate the likelihood of future events based on historical data.
- Quality control:To monitor and improve production processes by identifying defects and non-conformities.
- Epidemiology:To study the distribution of diseases and risk factors in populations.
- Marketing:To understand customer preferences, segment markets, and optimize marketing campaigns.
Popular Questions
What is the purpose of a table of relative frequencies?
A table of relative frequencies provides a clear and concise summary of the distribution of data, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data set.
How do I calculate relative frequencies?
Relative frequencies are calculated by dividing the frequency of each outcome by the total number of outcomes in the data set.
What is the importance of using appropriate table formatting?
Appropriate table formatting ensures that the table is easy to read and understand, making it more effective in communicating the data distribution.