Condensed structural formula for 1 4-dichlorocyclohexane – The condensed structural formula for 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane, C6H10Cl2, succinctly represents the molecular structure of this versatile compound. This formula provides a clear and concise depiction of the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, offering valuable insights into its properties and reactivity.
This Artikel delves into the intricacies of the condensed structural formula for 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane, exploring its relationship to the molecular structure, IUPAC nomenclature, physical and chemical properties, synthesis, and diverse applications. Along the way, we will uncover the significance of the chlorine atoms in shaping the characteristics of this important chemical compound.
Condensed Structural Formula: Condensed Structural Formula For 1 4-dichlorocyclohexane
A condensed structural formula is a representation of a molecule that shows the connectivity of the atoms but not all of the hydrogen atoms. The condensed structural formula for 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane is C6H10Cl2.
The condensed structural formula shows that the molecule has a cyclohexane ring with two chlorine atoms attached to the 1 and 4 positions. The carbon atoms in the ring are numbered from 1 to 6, and the chlorine atoms are attached to carbon atoms 1 and 4.
IUPAC Nomenclature
The IUPAC name for 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane is 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane.
The IUPAC name is based on the following rules:
- The base name of the compound is cyclohexane, which indicates that the compound has a six-membered ring of carbon atoms.
- The prefix “di-” indicates that there are two chlorine atoms attached to the ring.
- The numbers 1 and 4 indicate the positions of the chlorine atoms on the ring.
Physical and Chemical Properties
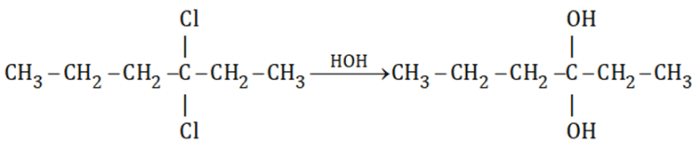
1,4-Dichlorocyclohexane is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 172 °C and a melting point of -10 °C. It is soluble in organic solvents but insoluble in water.
1,4-Dichlorocyclohexane is a reactive compound. It can undergo a variety of reactions, including addition, substitution, and elimination reactions.
The presence of the chlorine atoms on the ring makes 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane more reactive than cyclohexane. The chlorine atoms are electron-withdrawing groups, which means that they pull electrons away from the ring. This makes the ring more susceptible to attack by electrophiles.
Synthesis
1,4-Dichlorocyclohexane can be synthesized by a variety of methods. One common method is the reaction of cyclohexane with chlorine gas.
The reaction is carried out in the presence of a radical initiator, such as benzoyl peroxide. The radical initiator generates free radicals, which react with the chlorine gas to form chlorine atoms. The chlorine atoms then react with the cyclohexane to form 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane.
Applications
1,4-Dichlorocyclohexane is used as a solvent, a cleaning agent, and an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals.
As a solvent, 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane is used to dissolve a variety of organic compounds. It is also used as a cleaning agent to remove grease and oil from surfaces.
As an intermediate, 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane is used in the synthesis of a variety of other chemicals, including pesticides, herbicides, and pharmaceuticals.
FAQs
What is the IUPAC name for 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane?
The IUPAC name for 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane is 1,4-dichlorohexahydrobenzene.
What is the relationship between the condensed structural formula and the molecular structure of 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane?
The condensed structural formula shows the arrangement of atoms within the molecule, while the molecular structure provides a three-dimensional representation of the molecule, including bond lengths and angles.
How does the presence of chlorine atoms affect the properties of 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane?
The chlorine atoms increase the density, boiling point, and polarity of 1,4-dichlorocyclohexane compared to cyclohexane.