As Minimum Internal Temperature Mystery Picture takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. The significance of minimum internal temperature in food safety cannot be overstated, as it plays a pivotal role in preventing foodborne illnesses.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of minimum internal temperature, exploring its implications for food safety, the potential consequences of consuming undercooked foods, and the essential practices for preventing contamination.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Minimum Internal Temperature

Minimum internal temperature refers to the temperature that food must reach during cooking to ensure the destruction of harmful bacteria. It is a critical aspect of food safety, as consuming undercooked foods can lead to foodborne illnesses.
Examples of Minimum Internal Temperatures
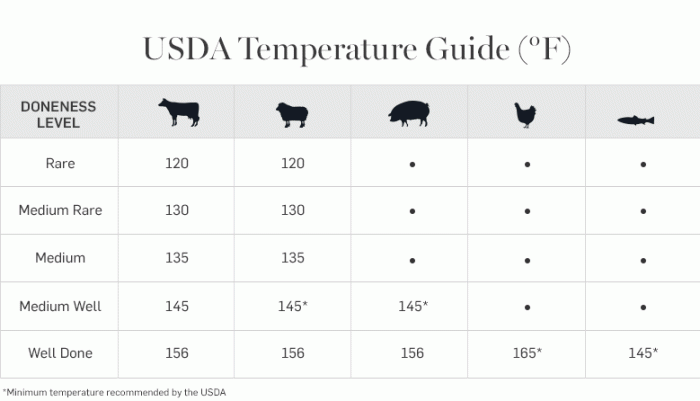
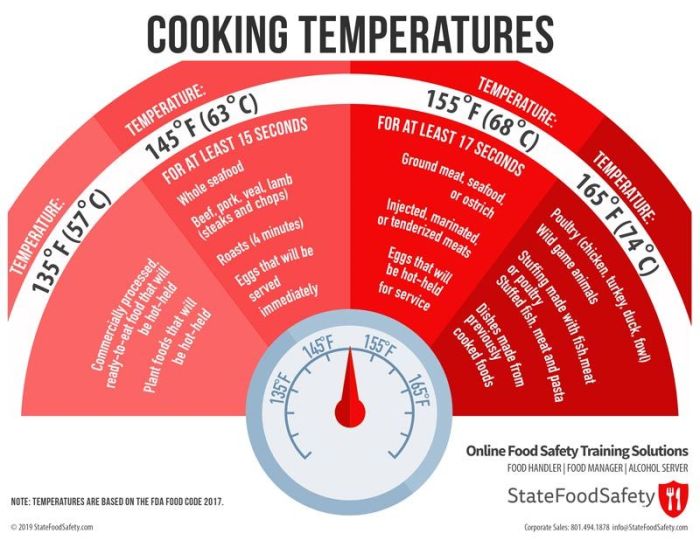
- Poultry (chicken, turkey): 165°F (74°C)
- Ground beef, pork, lamb, veal: 155°F (68°C)
- Fish and seafood: 145°F (63°C)
- Eggs: 160°F (71°C) for yolks
Consequences of Consuming Undercooked Foods
- Foodborne illnesses (e.g., salmonella, E. coli)
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- Severe dehydration, hospitalization, or even death in extreme cases
Foodborne Pathogens
Foodborne pathogens are microorganisms that can cause illness when consumed through contaminated food. Common pathogens include:
- Salmonella
- Escherichia coli (E. coli)
- Campylobacter
- Listeria monocytogenes
Contamination Sources
- Animal products (e.g., poultry, meat, eggs)
- Produce (e.g., fruits, vegetables)
- Unpasteurized milk and dairy products
- Contaminated surfaces and utensils
Symptoms and Severity
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Fever
- In severe cases, hospitalization or even death
Food Handling Practices
Proper food handling practices are crucial to prevent contamination and ensure food safety. Key practices include:
Washing Hands, Surfaces, and Utensils
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after handling food
- Clean and sanitize all surfaces and utensils that come into contact with food
Temperature Control
- Keep cold foods cold (below 40°F or 4°C)
- Keep hot foods hot (above 145°F or 63°C)
- Avoid leaving food at room temperature for extended periods
Cooking Techniques: Minimum Internal Temperature Mystery Picture
Effective cooking techniques can kill bacteria and ensure food safety. Common methods include:
Grilling, Roasting, and Baking, Minimum internal temperature mystery picture
- Reach internal temperatures as specified in the minimum internal temperature guidelines
Boiling
- Boil liquids to a rolling boil for at least 1 minute
Microwaving
- Use a food thermometer to ensure even cooking and reaching safe internal temperatures
Food Storage
Proper food storage is essential to prevent bacterial growth and maintain food quality. Key practices include:
Refrigeration
- Store perishable foods in the refrigerator at or below 40°F (4°C)
- Follow recommended storage times for different foods
Freezing
- Freeze foods at or below 0°F (-18°C)
- Freezing does not kill bacteria but stops their growth
Vacuum Sealing
- Vacuum sealing removes oxygen, which inhibits bacterial growth
General Inquiries
What is the significance of minimum internal temperature in food safety?
Minimum internal temperature plays a critical role in ensuring food safety by eliminating harmful bacteria that can cause foodborne illnesses.
What are some examples of foods with specific minimum internal temperatures?
Examples include poultry (165°F), ground beef (155°F), and fish (145°F).
What are the potential consequences of consuming undercooked foods?
Consuming undercooked foods can lead to foodborne illnesses, causing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain.