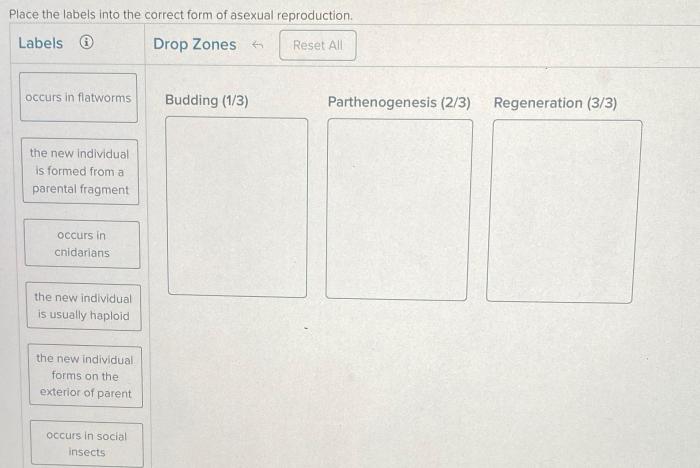
Place the labels into the correct form of asexual reproduction. – In the realm of biological sciences, asexual reproduction stands as a fascinating phenomenon, allowing organisms to perpetuate their lineage without the fusion of gametes. Delving into the intricacies of this reproductive strategy, this discourse explores the diverse forms of asexual reproduction, unraveling their mechanisms, advantages, and limitations.
From the simplicity of binary fission to the complexities of parthenogenesis, asexual reproduction exhibits a remarkable array of adaptations, enabling organisms to thrive in a multitude of environments. This discourse will delve into the intricacies of each form, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental biological process.
Asexual Reproduction: Place The Labels Into The Correct Form Of Asexual Reproduction.
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction in which an organism creates a genetically identical copy of itself without the involvement of another organism. This process is common in many organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and plants. Asexual reproduction can occur through a variety of mechanisms, including binary fission, budding, fragmentation, parthenogenesis, and spore formation.
Binary Fission
Binary fission is the simplest form of asexual reproduction. In this process, the organism simply divides into two equal parts, each of which then becomes a new individual. Binary fission is common in bacteria and other unicellular organisms.
Advantages of Binary Fission:
- It is a rapid and efficient way to reproduce.
- It produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.
Disadvantages of Binary Fission:
- It can only occur in organisms that are small and simple.
- It can lead to a rapid population growth, which can be a problem in some environments.
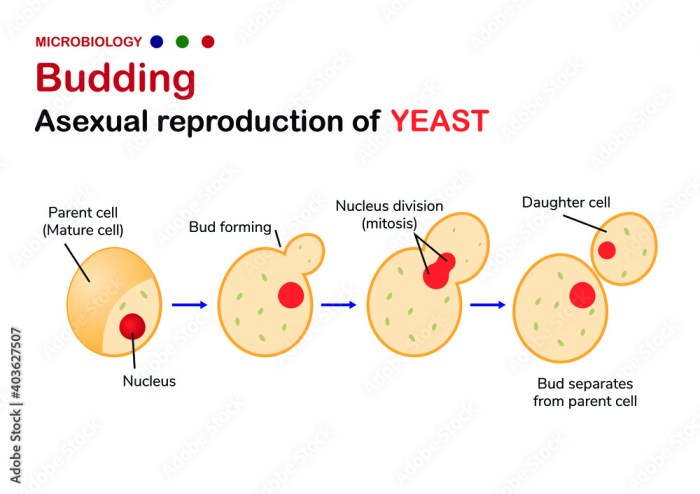
Budding
Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism grows out of the body of the parent organism. The new organism is initially attached to the parent, but it eventually breaks away and becomes an independent individual.
Budding is common in yeasts and other fungi.
Differences between Budding and Binary Fission:
- In budding, the new organism grows out of the body of the parent, while in binary fission, the parent organism divides into two equal parts.
- In budding, the new organism is initially attached to the parent, while in binary fission, the two new organisms are immediately separate.
Fragmentation
Fragmentation is a type of asexual reproduction in which an organism breaks into several pieces, each of which then grows into a new individual. Fragmentation is common in plants and some animals.
Environmental Factors that can Influence Fragmentation:
- Temperature
- Light
- Water availability
Parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which an organism develops from an unfertilized egg. Parthenogenesis is common in some plants, animals, and insects.
Types of Parthenogenesis:
- Arrhenotoky:Unfertilized eggs develop into males.
- Thelytoky:Unfertilized eggs develop into females.
- Amphitoky:Unfertilized eggs can develop into either males or females.
Advantages of Parthenogenesis:
- It allows organisms to reproduce without a mate.
- It can lead to the rapid population growth of a species.
Disadvantages of Parthenogenesis:
- It can lead to a loss of genetic diversity.
- It can make a species more vulnerable to disease.
Spore Formation, Place the labels into the correct form of asexual reproduction.
Spore formation is a type of asexual reproduction in which an organism produces spores. Spores are small, dormant cells that can survive harsh conditions. When conditions are favorable, the spores can germinate and grow into new individuals. Spore formation is common in fungi, bacteria, and some plants.
Types of Spores and their Functions:
- Conidia:Asexual spores produced by fungi.
- Endospores:Dormant spores produced by bacteria.
- Zoospores:Motile spores produced by some algae and fungi.
Detailed FAQs
What are the key differences between binary fission and budding?
Binary fission involves the division of a single parent cell into two identical daughter cells, while budding entails the formation of a new individual as an outgrowth of the parent organism.
Can asexual reproduction occur in all types of organisms?
No, asexual reproduction is primarily observed in simpler organisms such as bacteria, protists, and some invertebrates, while sexual reproduction is more common in complex organisms.
What are the environmental factors that can influence fragmentation?
Environmental factors such as temperature, pH, and nutrient availability can influence the rate and success of fragmentation.